Fig. 1. General structure of audiovisual speech synthesis in a text
Main Sector of relevance\IRC classification 5. Electronics, IT and Telecommunication
5.8 System of audiovisual speech synthesis in a text “MULTIPHONE”
Developers’ contact information
State Scientific Institution “The United Institute of Informatics Problems of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus”
6 Surganova Str., 220012 Minsk
Summary
MULTIPHONE is a high technology software product realizing model of oral reading of any text by a human being. From user’s point of view MULTIPHONE is a new device for voice information output from PC adding and sometimes replacing visual data output on display. Now using MULTIPHONE a PC user can decrease eyestrain since receiving a part of the information in oral form. Besides he/ she can receive information being in motion at some distance from a computer, and, if using an additional telephone interface, he/ she can receive or transmit voice information by the phone. MULTIPHONE is a unique information transmittance device for blind people and an excellent possibility for computer systems for spoken language training.
Description
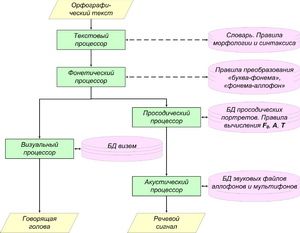
General structure of an audiovisual speech synthesis system under
text is presented on Fig. 1. Input orthographic text is consistently
transformed by several processors (textual, phonetic, prosodic, acoustic and
visual.
A textual processor is used for transformation of input orthographic text in a
prosodically marked text. The processor performs the following tasks:
- text splitting into sentences;
- conversion of numbers, abbreviation, acronyms, etc.;
- sentence splitting into prosodic syntagms;
- strong and weak stresses distribution;
- syntagm splitting into accentual units (AU);
- determining type of intonation syntagm.
A prosodically marked text is transmitted to a phonetic processor which
performs the following tasks:
- transformation of orthographic text into a phoneme sequence;
- transformation of a phoneme sequence into an allophonic sequence.
Formed allophonic sequence is transmitted to inputs of prosodic and visual
processors.
A prosodic processor performs the following tasks:
- AU splitting into accentual unit elements (AUE): pre-core, core and
after-core;
- estimation of desired bass frequency value (Fo), amplitude (A) and allophone
length (T) in accordance with accentual units images for each AU.
Acoustic processor uses information received from phonetic and prosodic
processors to perform the following operations:
- modification of prosodic parameter of allophone and multiphone
soundwaves;
- concatenation of allophone and multiphone soundwaves in a corresponding
sequence.
A visual processor uses information received from a phonetic processor to
choose required visems and their concatenation in the database.

Technology type
Technical advantages and economic benefits
- Top-rank synthesized speech audibility;
- Automatic intoning during speech synthesis in a text;
- High naturalness and expression of text reading;
- High quality of 2 male and 2 female voices synthesis;
- Possibility to clone personal voice and reading manner;
- Possibility to add new voice and intonation styles;
- Bilingual speech synthesis. Language: Russian, Belarusian;
- Possibility to add new languages;
- Visual image speech gestures – “Talking Head”;
- Possibility of image personalization – “Talking Head”;
- Possibility to build system into external applications under standard SAPI
5.1.
System requirements:
- Windows OS;
- Processor: Intel Pentium 233 mHz (minimum);
- Memory/ RAM: 32 Mb (minimum);
- Hard drive space: 64 Mbyte (minimum).
Technology differentiation and uniqueness
- Internet-services by the phone – reading e-mail messages and
other services;
- Phone reference systems – “call centers"
- Mobile telephony (SMS vocalization);
- Phone systems for automatic informing;
- Speech accompaniment of CAD task solution;
- Voice announcement in transport, at railroad stations and in airports;
- Voice prompts during pictures editing
- Step-by-step vocal installation and setting-up instructions;
- Electronic books reading;
- Tables and texts auditory monitoring;
- Speaking advertising videoclips;
- Langue and parole computer-managed instruction system;
- Speaking computer for visually handicapped;
- Development of a vocal offenders clone bank;
- Real time evidence of a person by voice;
- Voice simulation movie and video production;
- Systems of individualized announcement;
- Distance learning with virtual instructor voice;
- Intellectual virtual interlocutors;
Context in which technology was identified
13th, 14th and 15th International Specialized Exposition on Telecommunications, Information and Bank Technologies, Security Systems TIBO’2006, TIBO’2007, TIBO’2008. Periodical expositions of the National Academy of Science of Belarus.
Technological keywords
Speech, voice, voice interface, speech synthesis, voice announcement
Development Stage
Intellectual property rights
Range of applications
Computer and telecommunication systems.
Classifier Used at the EU Innovation Relay Centres
Preferable Regions
Practical experience
Subsystem of speech synthesis in a text is used in the following
software systems:
- system of automated abstracting and vocalization of text-based documents;
- dedicated system for electronic book reading by blind and starblind persons
“Electronic Speaking Library";
- system of creation and audio books listening with mobile phone.
Subsystem of audio-visual speech synthesis in a text will be used in a
multimodal information kiosk having a dialogue with a user in human language by
video-, sound and textual channels.
Environmental impact
None.
Type of collaboration sought
Terms and restrictions
Under agreement or license
Available technical assistance